Our fabulous registered kinesiologist Kheya McGill is back! In part 1 of her two-part blog series, Kheya reviews her favourite mobility and stretching exercises to help you tackle your neck and back pain. For Kheya’s favourite strengthening exercises, visit Part 2.
Neck and back pain are very common conditions. Sinnott et al. found that, at any given time, 15-20% of us will report back pain and 10-20% of us will report neck pain. Those numbers are huge! Spending more time hunched over computers (like most of us have been over the past two years) hasn’t helped.
Taking movement breaks throughout the day can be incredibly helpful for keeping pain at bay. It really boils down to the saying “motion is lotion” - the more you move your body, the easier (and less painful) it is to move. If you’re able to, taking a quick break every hour can make all the difference.
In this blog I will outline a few of my favourite exercises to increase spinal mobility and stretch tight back muscles. Make sure to stay tuned for part 2 of my blog series on neck and back pain, which will focus on my favourite strengthening exercises.
But first, a review of spinal anatomy…
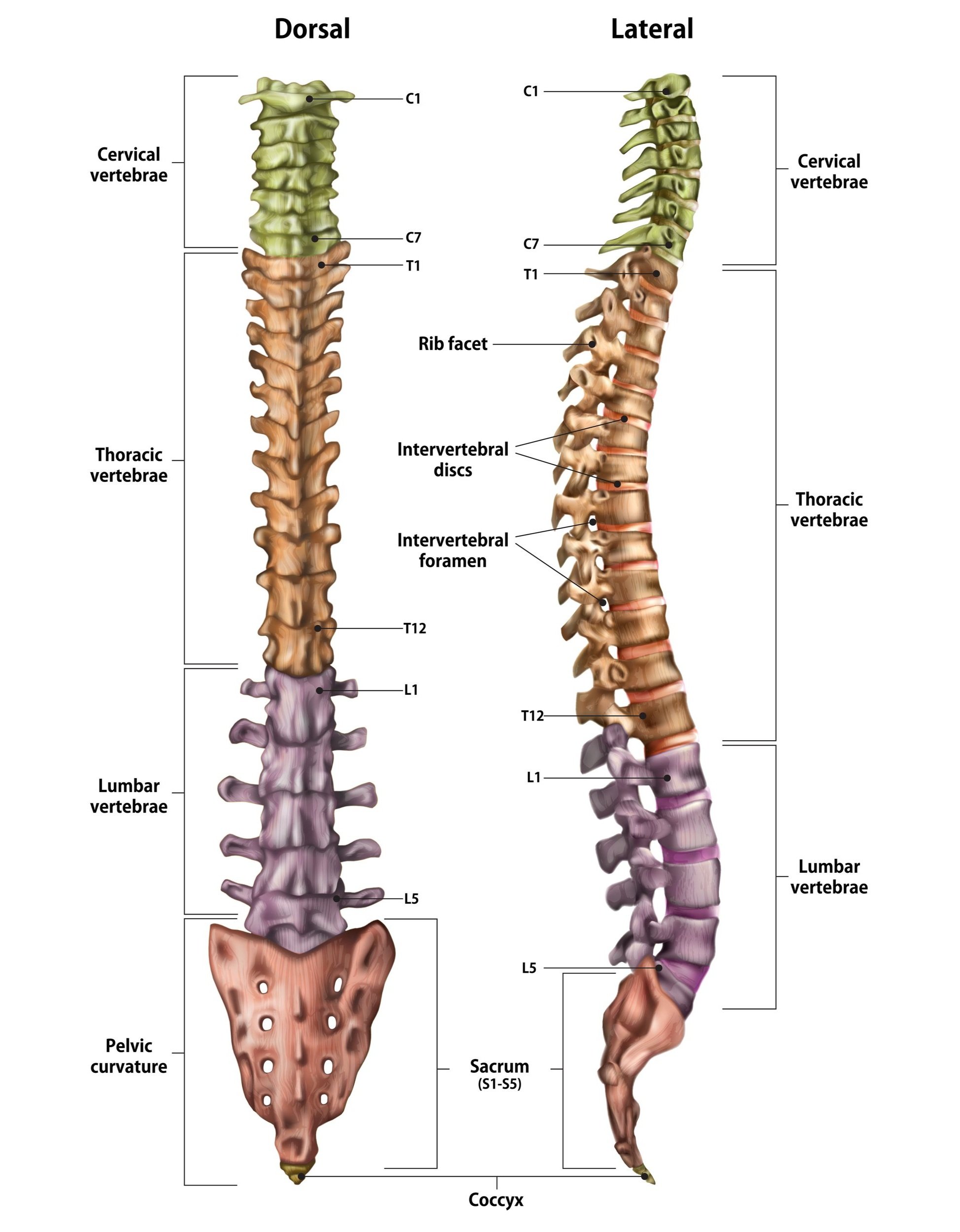
Our spine is organized into 5 main regions. From the head down, these regions are:
cervical spine - 7 vertebrae that make up the neck
thoracic spine - 12 vertebrae in the upper and mid-back, all of which attach to ribs
lumbar spine - 5 vertebrae of the low back
sacral spine - 5 vertebrae fused to form the sacrum, the triangular bone that helps make up the pelvis
coccyx - also known as the tailbone, located at the very bottom of the spine
The spine has three main jobs:
Central supporting structure - the spine acts as a scaffold for your body. Muscles, ligaments and connective tissue attach to each vertebra of the spine and to the limbs. The rigidity of the spine also holds us up against gravity.
Protector of the spinal cord - millions of nerve cells travel up and down your spinal cord, sending signals up to the brain and out to the entire body. Without the bony protection of the vertebrae, the spinal cord would be much more vulnerable to trauma and injury.
Movement - the multiple joints of the spine allow a lot of movement to occur including sitting, standing, walking, bending forward and twisting around.
Keeping your spine healthy is critical to your overall health - the stronger and more mobile you are, the better!
Kheya’s Top Five Mobility and Stretching Exercises
The Mobility Exercises
What is it:
Mobility refers to the ability of a joint to move actively through a range of motion (see our previous post on flexibility vs. mobility for more on this). Improving mobility helps increase the range of motion available in the joints, leading to improved function and decreased pain.
1) Thoracic spine openers
Begin by laying on your side with your legs slightly bent and stacked on top of each other. Stretch your arms out straight in front of you. Keeping your bottom arm on the floor, roll on your back and sweep your arm up and over to the other side, opening the chest. Keep your eyes on the top hand, rotating your neck as your arm rotates over your body. Once you have reached your end range, bring your arm back across your body.
Repeat 5-10 times per side.
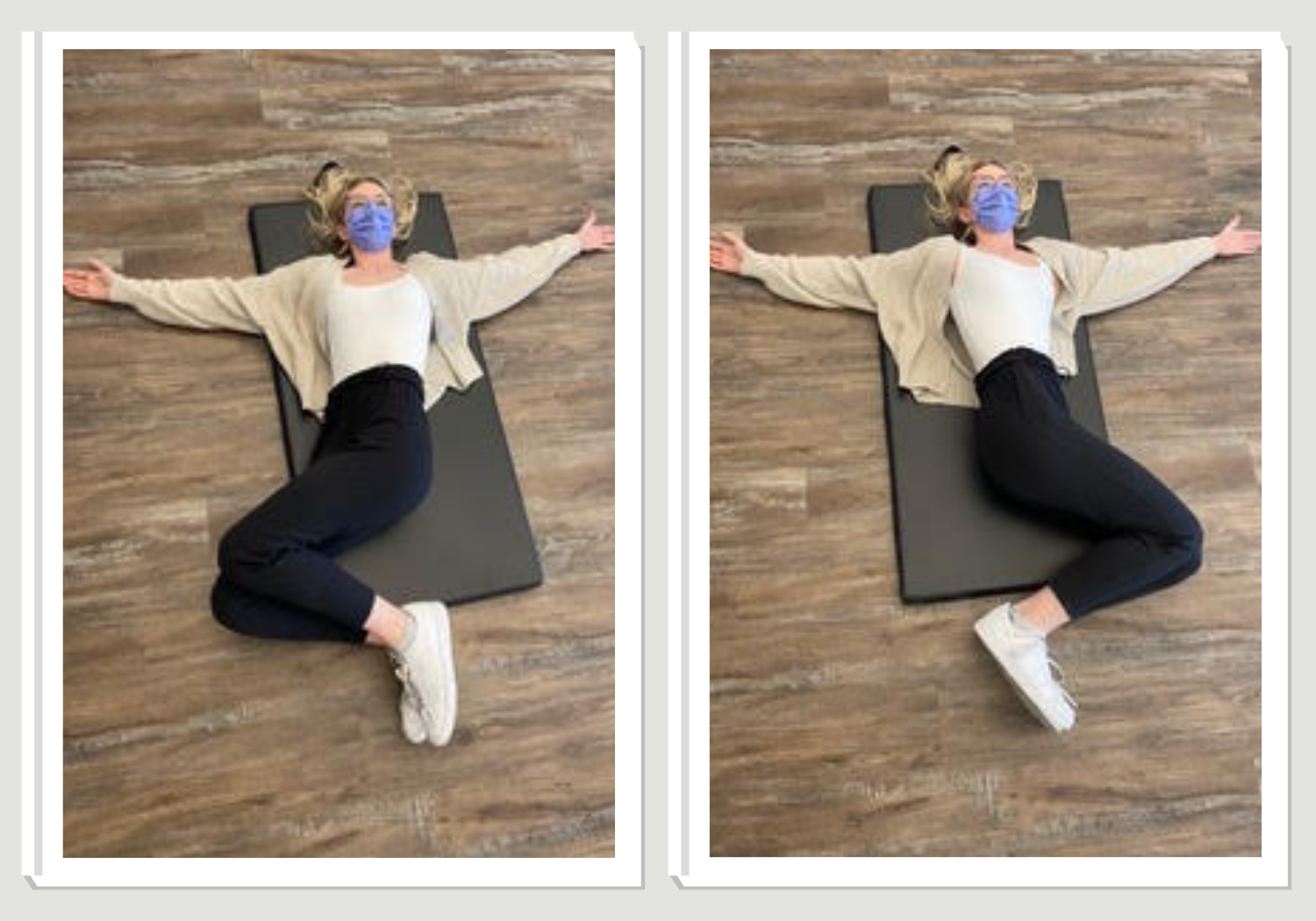
2) Lumbar rotation
Begin on your back with your knees bent, feet flat on the floor and your arms stretched out on either side of you like a “T”. Keeping your back flat on the ground, drop both legs out to one side. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds. Bring your knees back to the middle and then repeat the same movement on the opposite side.
Repeat this movement 10 times for 2-3 sets.
3) Cat cow
Begin on all fours. With the hands underneath the shoulders, lift your head and chest while simultaneously letting your stomach sink and lower back arch. After this, switch and round the back and let the head and neck drop while rounding your back as much as possible.
Repeat these alternating movements 10 times and then repeat this for 2-3 sets.
The Stretches
Stretching is the ability to move muscles through a range of motion passively. In other words, pushing to get to the joints through the end range using assistance from your hands, the wall, a strap, or anything else (see our previous post on flexibility vs. mobility for more on this). Stretching is useful for back pain as it can help loosen sore and tight muscles.
1) Childs pose
Begin on your hands and knees and drop your bum back onto your heels. Reach your hands forwards, dropping your head and shoulders down towards the floor.
Hold for 20-30s and repeat 2-3 times.
2) Knee hugs
Begin laying on your back and hug one leg in towards your chest.
Hold this for 20-30s. Repeat on both sides and complete 2-3 sets.
Next up, the strengthening exercises! Head over to Part 2 for my favourite exercises to make your body stronger.
If you are unsure of where to start, our registered kinesiologists would be happy to work with you to create an exercise program which matches your exercise goals and injury specific recovery needs.
Give us a call today give us a call at (778) 630-8800, email us or book online to seek treatment from a physiotherapist or to work with a registered kinesiologist.